C:\java>javac SimpleGUI.java C:\java>java SimpleGUI
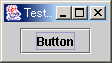 |
図:SimpleGUI の実行結果 |
last modified: Jun./30th/2002; Since: Jan./22nd/2002
コンポーネントの文字色、背景色を指定できます。それには java.awt.Component クラスのメソッドを用います。殆どの Swing コンポーネントはこのクラスを継承しているので、これらのメソッドが使えます。
| メソッド | 戻り値 | 概要 |
|---|---|---|
setBackground(java.awt.Color) | なし | コンポーネントに背景色をセットします。 |
getBackground() | java.awt.Color |
コンポーネントの背景色を返します。 |
setForeground(java.awt.Color) | なし | コンポーネントに前景色をセットします。 |
getForeground() | java.awt.Color |
コンポーネントのの前景色を返します。 |
java.awt.Color クラスでは13色の色名が静的メンバ変数として利用できますが、 sRGB 256 進でも指定できます。
次のアプリケーションに色を指定してみましょう。
SimpleGUI.java:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
class SimpleGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// フレームのインスタンス化
JFrame win = new JFrame("TestColor");
// パネルのインスタンス化
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
// ボタンのインスタンス化
JButton button = new JButton("Button");
// パネルにボタンを追加
panel.add(button);
// フレームからコンテントペインの取得
Container cont = win.getContentPane();
// コンテントペインにパネルを追加
cont.add(panel);
// フレームのセットアップ
win.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
win.pack();
win.setVisible(true);
}
}
実行例:
C:\java>javac SimpleGUI.java C:\java>java SimpleGUI |
|
この Swing GUI アプリケーションのパネルとボタンに、色を指定します。色の指定は、 Color クラスの予約済みのキーワードを使うか、 RGBs 値を指定した Coloe オブジェクトを作成して、対象のオブジェクトに指定します。
TestColor.java:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
class TestColor{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame win = new JFrame("TestColor");
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
JButton button = new JButton("Button");
// Color オブジェクトの作成と指定
panel.setBackground(Color.white);
button.setBackground(Color.cyan);
button.setForeground(new Color(50, 50, 200));
panel.add(button);
Container cont = win.getContentPane();
cont.add(panel);
win.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
win.pack();
win.setVisible(true);
}
}
実行例:
C:\Java>javac TestColor.java C:\Java>java TestColor |
|
フォントの種類や大きさも同様に指定できる。
| メソッド | 戻り値 | 概要 |
|---|---|---|
setFont( | なし | コンポーネントにフォントをセットします。 |
getFont() | java.awt.Font |
コンポーネントのフォントを返します。 |
java.awt.Font クラスは「フォント名、スタイル名、ポイントサイズ」の三つを指定してフォントを表せます。
public Font(String name, int style, int size)
二つ目の引数のフォントスタイルは、 PLAIN, ITALIC, BOLD の三つが許されます。
一つ目の引数に許されるフォント名はシステムによって異なります。但し、論理名として Dialog、DialogInput、Monospaced、Serif、SansSerif、または Symbol のうちの 1 つが利用できて、 null の場合、新しい Font の 名前 が Default になります。
GraphicsEnvironment クラスの getAvailableFontFamilyNames() メソッドは、システムで使用できるすべてのフォントファミリー名の配列を返します。
AllFont.java:
import java.awt.*;
class AllFont{
public static void main(String args[]){
String fonts[]
= GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment().
getAvailableFontFamilyNames();
for(int i=0;i<fonts.length;i++){
System.out.print(fonts[i]);
System.out.print(": ");
}
}
}
C:\Java>javac AllFont.java C:\Java>java AllFont Arial: Arial Black: Arial Narrow: Arial Unicode MS: Batang: BatangChe: Book Anti qua: Bookman Old Style: Bookshelf Symbol 1: Bookshelf Symbol 2: Bookshelf Symbol 3: Bookshelf Symbol 4: Bookshelf Symbol 5: Century: Century Gothic: Comic Sans MS: Courier New: Default: Dialog: dialog.plain: DialogInput: dialoginput.plain: ...中略... ans Unicode: Marlett: Microsoft Sans Serif: Monospaced: monospaced.plain: MS Out look: MS UI Gothic: OCRB: Palatino Linotype: SansSerif: sansserif.plain: Serif: serif.plain: SimSun: Symbol: Tahoma: Times New Roman: Trebuchet MS: Verdana: Web dings: Wingdings: 新細明體: 細明體: MS ゴシック: MS 明朝: MS Pゴシック: MS P明朝: MS PRゴシック: MS PR2ゴシック:
この実行結果は、私がいまたまたま使っているシステムの環境であって、一般性は全くありません。
TestFonts.java:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
class TestFonts implements SwingConstants{
public static void main(String args[]){
// トップレベルコンテナ
JFrame frame = new JFrame("TestFonts");
// 中間コンテナ
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
// アトミック・コンポーネント
JButton button1 = new JButton("Default 12 を指定");
JButton button2 = new JButton("Serif BOLD 15 を指定");
JButton button3 = new JButton("Set \"Times New Roman ITALIC 15\"");
JButton button4 = new JButton("Set \"Arial ITALIC|BOLD 12\"");
// フォント・オブジェクトの作成
Font font1 = new Font("Default", Font.PLAIN, 12);
Font font2 = new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 15);
Font font3 = new Font("Times New Roman", Font.ITALIC, 15);
Font font4 = new Font("Arial", Font.ITALIC|Font.BOLD, 12);
// コンポーネントにフォントを指定
button1.setFont(font1);
button2.setFont(font2);
button3.setFont(font3);
button4.setFont(font4);
// レイアウトマネージャの指定
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 3, 80, 20));
// 部品の配置
panel.add(button1);
panel.add(button2);
panel.add(button3);
panel.add(button4);
// コンテントペインの取得
Container cont = frame.getContentPane();
// 中間コンテナの配置
cont.add(panel);
// トップレベルコンテナのセットアップ
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
フォントの指定では、フォント・オブジェクトを作成して、対処のオブジェクトに指定します。
このサンプルで setFont() メソッド以外で注意すべき点は、レイアウト・マネージャに GridLayout を用いていることです。引数が四つあるコンストラクタを用いていますが、第一引数から順番に、「行数、列数、水平方向の空間、垂直方向の空間」が指定されています。横方向80、縦方向20の空間が指定されています。以下の例で、ボタン同士の間隔に注意してください。
C:\Java>javac TestFonts.java C:\Java>java TestFonts
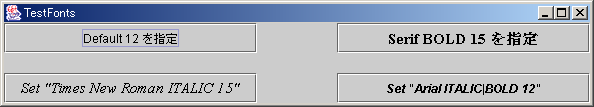 |
| 図:実行結果 |